To prepare engineering and manufacturing with the best start, it’s integral to choose an effective material that is not only high in quality, but can deliver results that meet a businesses tailored requirements. Aluminium and steel are two of the most commonly used metals across several key industries for a variety of applications. This guide develops an understanding of the differing properties between them, and how to choose the right metal for the project.
Quick Links
The Key Differences Between Aluminium and Steel
Weight and Density
There is a noticeable weight difference between the two metals, with aluminium being notably lighter than its steel counterpart. Aluminium has an approximate density of around 2.70 g/cm³, compared to steels 7.85 g/cm³, resulting in a weight that is roughly one-third of steel. This is valuable in sectors where weight is a major factor in design, most notably in automotive and aerospace sectors where fuel efficient and lightweight material are essential.
Durability
Steel typically exceeds aluminium when demonstrating a strength-to-weight ratio due to its high amount of carbon that reinforces the alloy’s structure. This makes steel preferable for applications that require robust components with high tensile strength. However, aluminium has the capacity to maintain the same weight load as steel in half the weight, particularly in cold room applications, but this does result in larger structures.
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminium has a slight edge over steel in terms of corrosion resistance. This is due to the naturally forming oxide layer that is established when exposed to air, resulting in aluminium not rusting or corroding over time. Alternatively, steel does not form a protective layer and is much more susceptible, leading to additional treatment to combat this issue. Other variants of steel, such as stainless steel, contain minor amounts of chromium to offer additional protection.
Conductivity
Aluminium comes out on top when it comes to thermal and electrical conductivity, which is why it’s commonly used for the structure of power lines, although it requires specialised skills to maintain the integrity for high-heat applications. Steel is known to be a poor conductor of electricity, and not quite up to par as aluminium in thermal. However, due to the high strength of steel, it can often handle higher temperatures without compromising the material integrity.
Fabrication
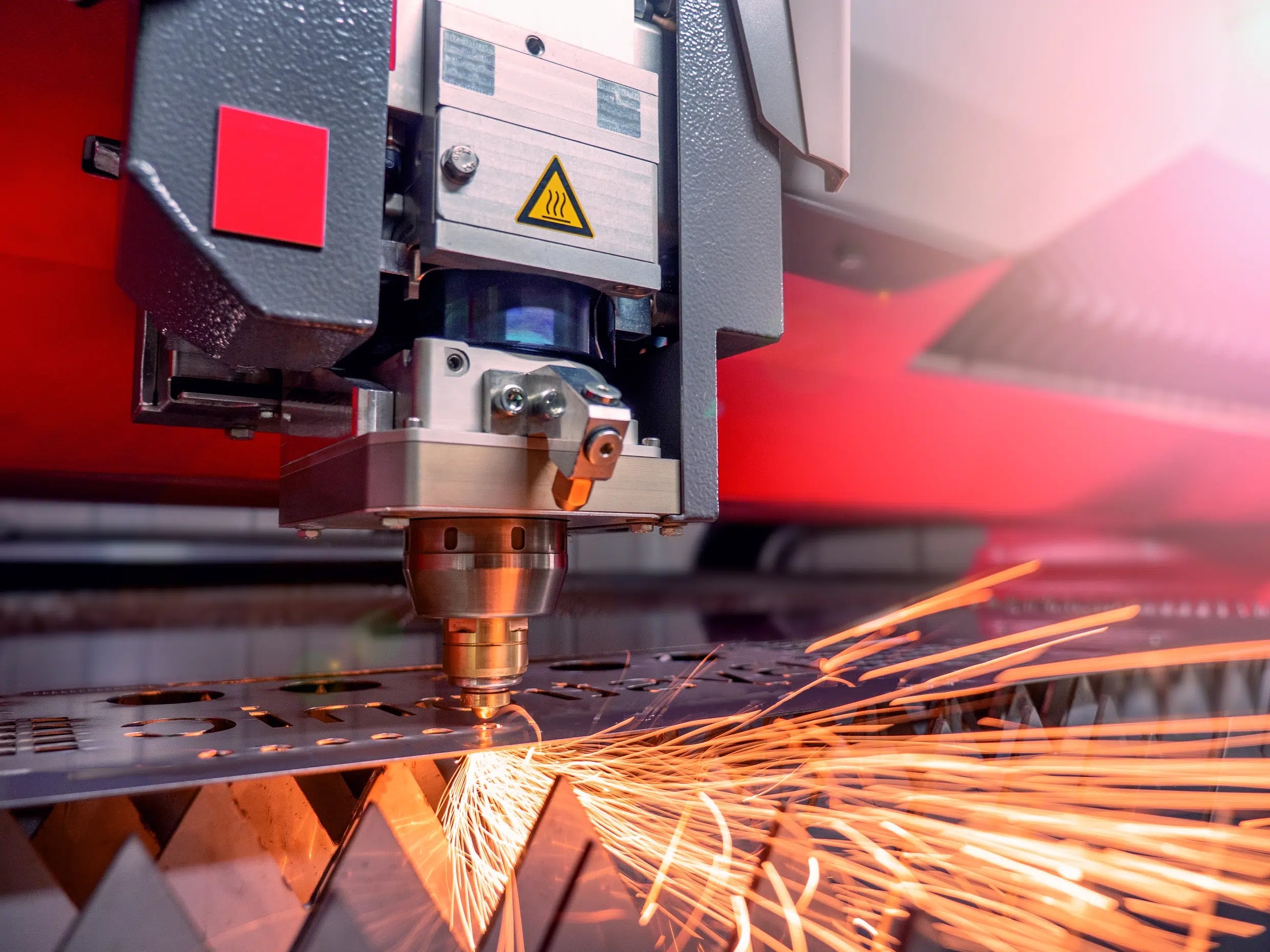
Generally, aluminium is a more malleable and ductile material, which makes it incredibly easy to process in various applications. This allows for processes such as laser metal cutting to create intricate and complex designs with ease. While steel can not be manipulated as easily, CAD technology and laser cutting machines are capable of fabricating steel sheets with high precision.
Cost Considerations
Steel is considered a more cost-effective option as a raw material, but can lead to inflated shipping costs due to its higher weight. Additionally, the price of aluminium can be slightly offset by its lightweight composition. It’s important to consider which metal type is most beneficial for the project; aluminium may have more long-term benefits if it proves to meet specialised requirements.

Applications of Aluminium and Steel
There can be a lot of overlap when it comes to utilising aluminium and steel, with a diverse range of capabilities and applications. Here are just some of the key sectors of both materials.
Aluminium
- Structural Components
- Aerospace and Automotive
- Electrical Structures and Parts
- Food and Beverage
- Household Appliances
- Architectural
- Marine
Steel
- Infrastructure
- Engineering
- Medical Equipment
- Hospitality
- Storage Tanks or Doors
- Household Goods
- Petrochemical Industry

How to Choose the Right Metal for the Project?
Before deciding on a material based on budget purposes, it’s important to recognise what the project requires and how this can affect the material type.
Environment
Will the metal be exposed to adverse weather elements or extreme temperatures that could cause corrosion or affect the structure?
Weight
Would the weight of the structure affect the outcome?
Fabrication Method
In processes such as laser cutting, understand which material is best suited to the service you choose. Different cutting methods can provide varying results across materials.
Strength
Is the metal durable and robust enough to meet the tailored requirements of your project? Likewise, is ductility important within the process?
Conductivity
Understand whether the material can fulfil a desired purpose, particularly when it is required to provide thermal and electrical conductivity.
Aesthetic
Will the finished product meet the aesthetic value intended for the project and can it process complex designs if required?

Discover Quality Aluminium and Steel Laser Cutting
Charles Day Steels provides leading metal profiling, delivering high-quality and precise mechanical, waterjet, flame, plasma, and laser cutting solutions for all projects, regardless of scale and complexity.
Our expansive portfolio encompasses dynamic, precise and high-quality results for all aluminium and steel requirements. As we continuously invest in the latest innovative technology, we are proud to deliver accuracy that is compliant and sustainable.
If you require metal profiling in rapid lead times, speak to a member of our team today for a no-obligation quote.